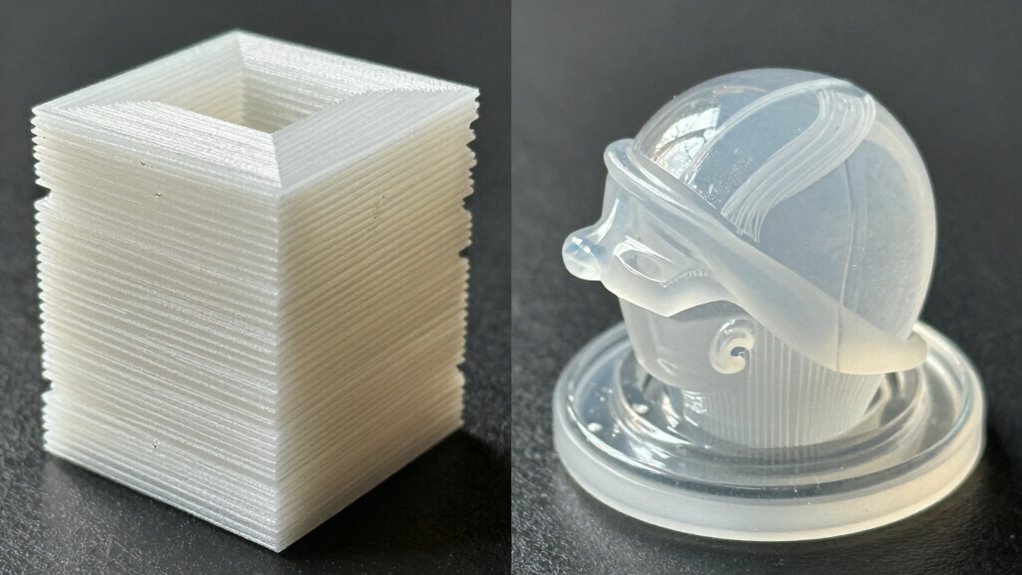
Choosing between FDM and resin 3D printing without proper understanding can lead to costly regrets. FDM offers durability, affordability, and faster production for larger parts, while resin provides high detail, smooth surfaces, and intricate features ideal for miniatures and jewelry. If you guess blindly, you might end up compromising on quality, cost, or time. Stick with the right method for your project, and you’ll make smarter decisions along the way. Learn more to choose wisely.
Key Takeaways
- Choosing resin over FDM may lead to brittle, impact-sensitive parts unsuitable for load-bearing applications.
- Opting for FDM instead of resin can result in lower detail and rougher surface finishes, affecting fine-detail projects.
- Relying on resin without considering environmental impact increases chemical waste and disposal hazards.
- Selecting FDM over resin might limit the ability to produce highly detailed, small, or intricate designs.
- Ignoring maintenance and material costs can cause unexpected expenses, making the wrong choice costly over time.
What Are FDM and Resin 3D Printing? An Overview

Have you ever wondered how 3D printers create detailed objects? FDM and resin printing are two popular methods, each with unique features. FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, uses thermoplastic filaments that melt and are extruded layer by layer. Resin printing, on the other hand, employs liquid resin cured by UV light for high precision. Material flexibility plays a role here—FDM filaments often offer more choices, while resin provides fine detail. However, maintaining your printer is essential; FDM units require regular nozzle cleaning and calibration, whereas resin printers need careful resin handling and cleaning of the build platform. Additionally, contrast ratio significantly impacts the quality of the final printed object by affecting color depth and detail. Moreover, understanding the safety considerations associated with resin handling is crucial for user safety and printer longevity.
How Do FDM and Resin 3D Printing Technologies Work?
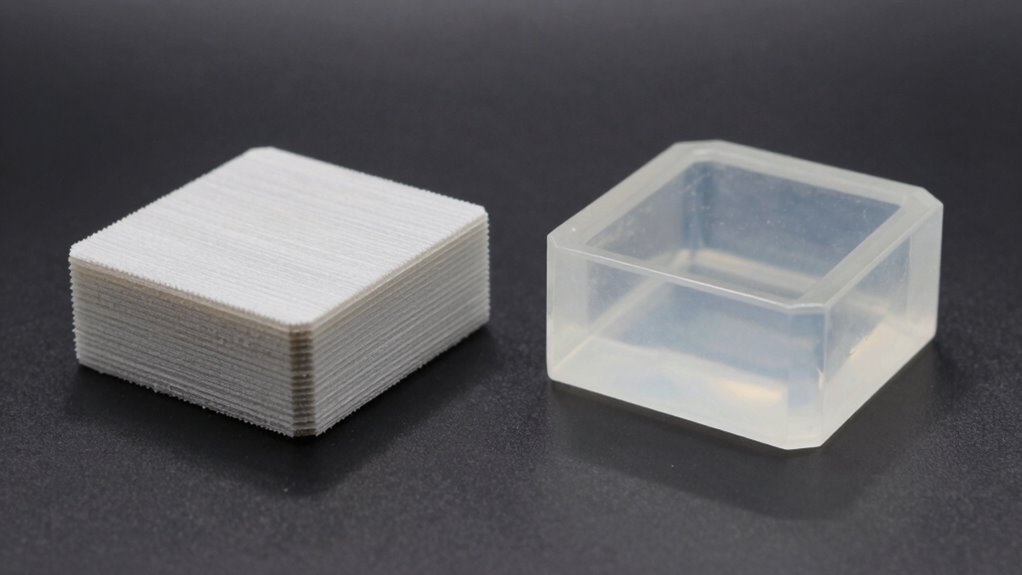
Understanding how FDM and resin 3D printers work involves examining their core mechanisms. FDM printers extrude melted thermoplastic filament layer by layer, shaping objects based on print orientation, which impacts strength and flexibility. Resin printers use a liquid photopolymer cured by light, building models layer by layer with high precision. Material flexibility varies: FDM parts can be more durable, while resin prints offer finer details. Print orientation influences surface finish and strength, especially in resin printing. Here’s a quick comparison: Print Orientation choices matter significantly for both technologies, affecting the final quality and performance of the printed objects.
Which Method Delivers Better Detail and Surface Finish?

When it comes to detail and surface finish, resin printing generally offers higher layer resolution and smoother surfaces. You’ll notice finer detail reproduction and less visible layer lines compared to FDM prints. This makes resin a better choice if precision and surface quality are your top priorities.
Layer Resolution Precision
Layer resolution plays a crucial role in determining the level of detail and surface quality in 3D printing. With higher layer resolution, you’ll achieve finer details and sharper edges, directly impacting print accuracy. Resin printers excel here, offering layer resolutions as low as 25 microns, which translates to smoother surfaces and intricate features. FDM printers typically have thicker layers, often between 100-300 microns, limiting their ability to capture fine detail. If you need precise, highly detailed models, resin printing provides superior layer resolution. However, keep in mind that the choice also affects print speed and complexity. Ultimately, for the best surface detail and accuracy, resin 3D printers deliver the edge, especially when capturing small features and delicate textures.
Surface Smoothness Quality
Surface smoothness quality is a key factor in choosing between FDM and resin 3D printing, as it directly affects the final appearance and tactile feel of your models. Resin printing consistently delivers superior finish quality, resulting in smoother surfaces with minimal layer lines. This high level of texture enhancement reduces post-processing time and enhances detail clarity. FDM prints often have visible layer lines and rougher surface textures, which can require extensive sanding or smoothing. If your goal is a polished, professional look straight off the printer, resin offers a significant advantage. While FDM provides durability and larger build volumes, resin’s ability to produce finer surface finishes makes it the preferred choice for detailed prototypes and display models. Ultimately, resin’s surface smoothness enhances the overall quality of your finished project.
Fine Detail Reproduction
Resin 3D printing excels at capturing fine details with remarkable accuracy, making it ideal for intricate models and highly detailed prototypes. Its ability to reproduce sharp features and smooth surfaces surpasses FDM, especially in small, delicate structures. Proper support structures are essential, as they prevent detail loss during printing and removal. Temperature control during resin curing ensures consistent layer adhesion and detail fidelity. Resin printers’ high resolution allows for smoother surface finishes, highlighting even minute features. Understanding print resolution is crucial, as it directly impacts the level of detail achievable in your prints. Additionally, resin printing’s layer curing process significantly influences the final surface quality, emphasizing the importance of precise exposure times and post-curing procedures. FDM struggles with fine detail due to filament extrusion limitations and layer stacking, which can obscure delicate features. While FDM is better suited for larger, rougher prototypes, resin printing offers superior detail reproduction when precision matters most, especially with well-managed support removal and stable temperature conditions.
What Material Options Are Available for FDM and Resin Printing? And Which Are Cost-Effective?
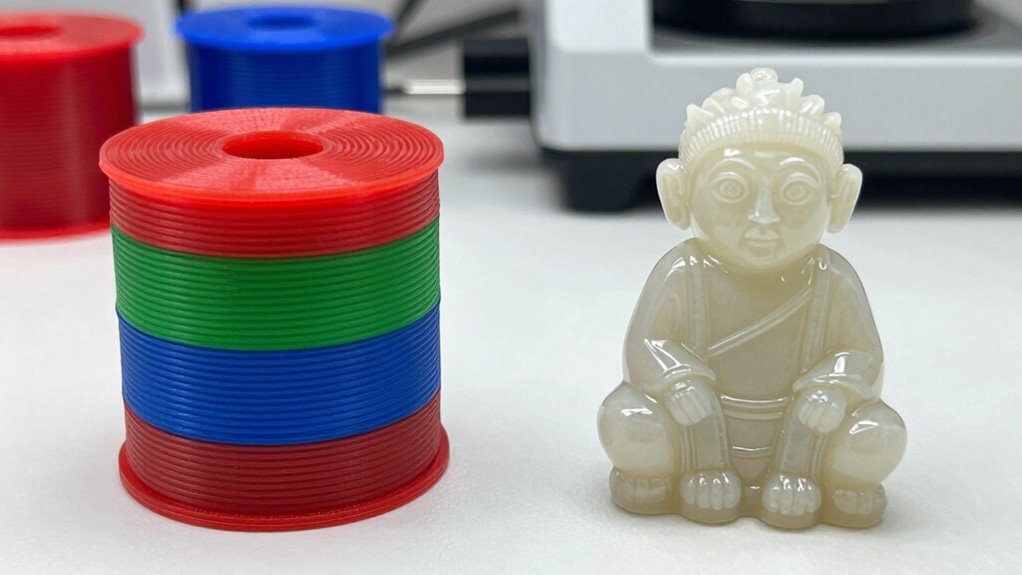

You have a range of materials to choose from for both FDM and resin printing, each with its own strengths and costs. Understanding the variety, prices, and compatibility can help you select the most cost-effective option for your project. Let’s explore what’s available and how to make the best choice for your needs. Additionally, Free Floating techniques can influence the selection process when designing for specific material properties and application environments. Being aware of material compatibility is crucial to ensure your chosen materials work seamlessly with your printer and project specifications. Recognizing material properties such as strength, flexibility, and curing requirements can further optimize your material choice and printing success.
Material Variety and Types
Both FDM and resin 3D printing offer a diverse range of materials, each suited for different applications and budgets. FDM materials include various thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU, offering good material compatibility for basic to advanced projects. Resin printing primarily uses photopolymer resins, which vary in flexibility, transparency, and strength. When choosing materials, consider chemical safety, as some resins contain potentially hazardous chemicals requiring proper handling. FDM filaments tend to be more cost-effective and easier to source, making them suitable for prototyping and functional parts. Resin materials, while often more expensive, provide higher detail and smoother finishes, ideal for jewelry, dental models, or detailed miniatures. Your choice depends on balancing material variety, safety, and budget constraints. Additionally, understanding material safety protocols is essential to ensure safe handling and disposal of resin substances.
Cost of Materials
When considering material options for 3D printing, understanding the cost differences between FDM and resin systems is essential. FDM materials, like PLA and ABS, generally have lower material costs, making them more budget-friendly for large or frequent projects. Resin materials tend to be more expensive per volume, often due to their specialized formulations for high detail and smooth finishes. Additionally, maintenance expenses differ: resin printers require regular cleaning of resin tanks and curing stations, which adds to ongoing costs, while FDM printers typically need less maintenance. If you’re prioritizing affordability, FDM offers a more cost-effective choice for materials and upkeep. Resin printing might be worth the investment for precision, but for general use, FDM keeps costs manageable.
Compatibility and Availability
FDM and resin 3D printers offer distinct material options that influence their suitability for different projects. Your choice depends on material compatibility and printer availability. FDM printers use thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, and PETG, which are widely available and cost-effective. Resin printers primarily work with photopolymer resins, offering high detail but limited material variety. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | FDM | Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Broad: PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU | Narrow: Photopolymer resins |
| Cost | Lower material costs | Usually more expensive |
| Printer Availability | Widely accessible and versatile | Less common, specialized equipment |
| Material Options | Many options for different uses | Limited, with high detail options |
| Cost-Effectiveness | More affordable for large projects | Better for detailed, small parts |
How Fast Can You Print? Speed and Production Volume for FDM vs. Resin
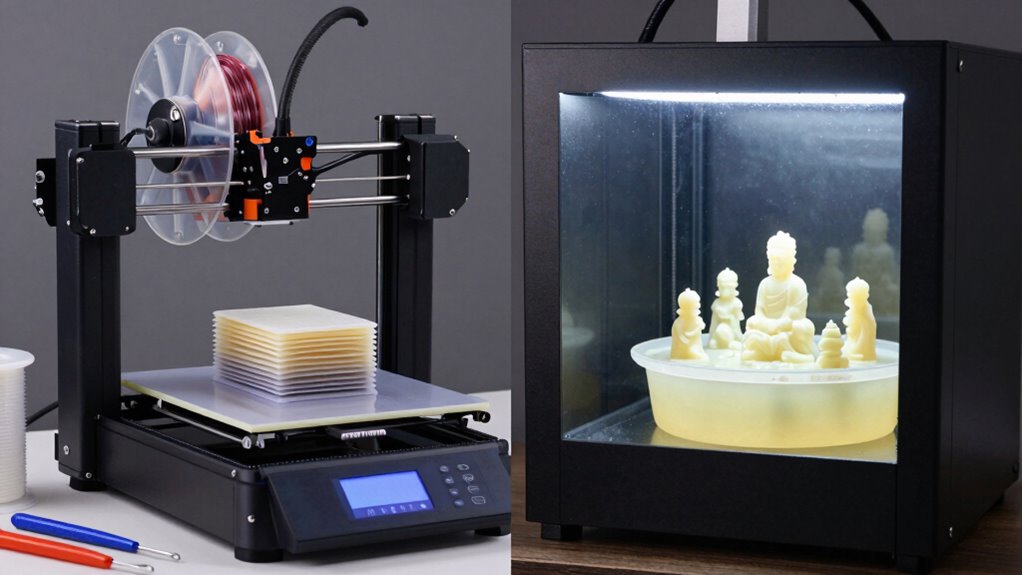

Understanding how quickly you can produce parts depends largely on the type of 3D printing you choose. FDM printers generally have a faster print speed for larger, less detailed objects, making them suitable for high production volume tasks. Resin printers, however, excel at detailed, smaller parts, but their print speed is slower because each layer requires curing time. If your priority is rapid turnaround for bulk items, FDM’s faster print speed and higher production volume capacity make it advantageous. Resin printing’s detailed resolution comes at the cost of slower print times, limiting its efficiency for large-scale production. Ultimately, your project’s speed requirements will determine whether FDM or resin printing best suits your needs.
How Do FDM and Resin Printing Compare in Strength, Durability, and Post-Processing?
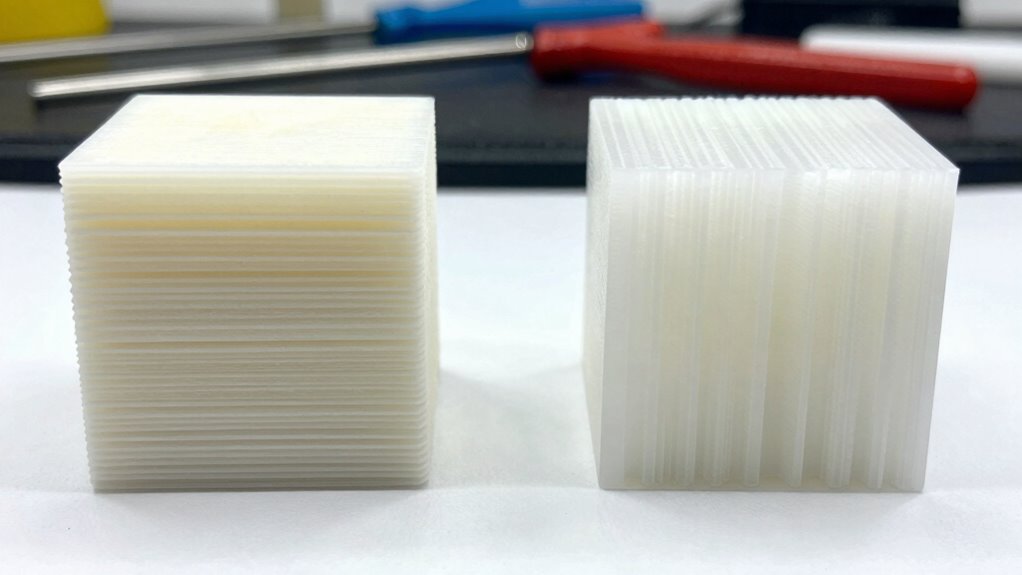
When comparing FDM and resin printing, you’ll notice differences in material strength and wear resistance that affect how long your prints last. Resin parts generally offer higher detail and durability but may require more complex post-processing. Understanding these factors helps you choose the right method for your specific needs. Additionally, selecting the appropriate essential gear can enhance your overall printing experience and outcomes.
Material Strength Differences
While both FDM and resin 3D printing produce functional parts, they differ significantly in strength and durability. FDM parts tend to be more flexible due to the nature of thermoplastic materials, making them suitable for applications requiring some give. Resin prints, on the other hand, are typically more rigid and brittle, offering higher detail but less impact resistance. Regarding material strength, FDM provides better durability for load-bearing uses, often at a lower cost efficiency, since filament options are generally cheaper and easier to handle. Resin parts excel in precision but may suffer from cracking or breaking under stress. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and cost efficiency or maximum detail and rigidity. Understanding these material properties can help you select the best printing method for your specific needs.
Wear and Tear Resistance
FDM and resin 3D printing differ markedly in their resistance to wear and tear, impacting how long parts last under repeated use. FDM prints generally offer better wear resistance and tear durability because of their layered filament structure, making them suitable for functional parts exposed to friction or mechanical stress. Resin prints, while highly detailed, tend to be more fragile and prone to surface damage over time. The resin’s brittle nature reduces tear durability, especially under repeated handling or stress. If you need parts that endure frequent use or harsh conditions, FDM is the better choice. Additionally, the layer adhesion in FDM prints contributes to their overall strength and longevity, making them more suitable for durable applications. Material properties play a significant role in determining the durability of each printing type, influencing how well they withstand wear over time. The post-processing requirements of resin prints can also affect their longevity, as improper handling can accelerate surface degradation. Resin parts are better suited for display or prototypes where surface finish and detail matter more than long-term durability. Proper curing techniques can improve the resilience of resin prints, but they still generally fall short compared to FDM in terms of wear resistance.
Post-Processing Complexity
Post-processing for FDM and resin 3D prints varies considerably in complexity, affecting how much time and effort you’ll need to achieve a finished part. FDM prints often require sanding, support removal, and sometimes painting, which can impact color accuracy. Resin prints, on the other hand, need careful cleaning with isopropyl alcohol and curing, making the process more delicate and time-consuming. Resin post-processing produces smoother surfaces and finer details but involves handling chemicals, raising environmental impact concerns. Resin post-processing also requires proper chemical disposal to minimize environmental harm. FDM post-processing is generally simpler but results in rougher finishes. Your choice influences not only the effort involved but also the environmental footprint, as resin printing tends to generate more waste and chemicals. Additionally, responsible use and privacy considerations are important when working with chemical-based resin processes. Ultimately, understanding these differences helps you choose based on your project’s durability, finish quality, and eco-consciousness.
How to Decide Between FDM and Resin 3D Printing for Your Project
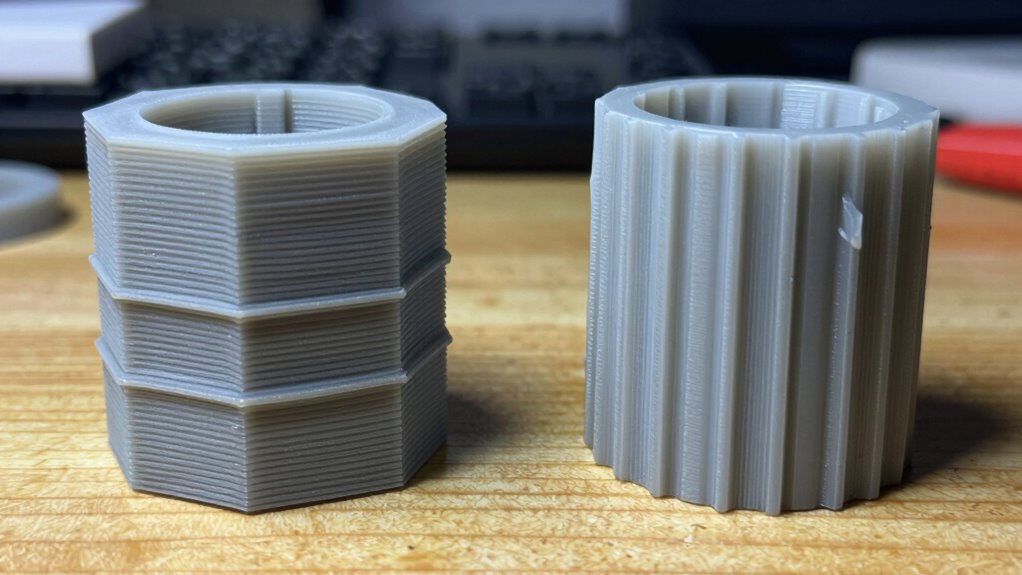
Choosing the right 3D printing method depends on your project’s specific needs and goals. To decide between FDM and resin printing, consider factors like cost comparison and environmental impact. FDM printers generally have a lower upfront cost and use filament, which produces less waste, making them more budget-friendly and eco-conscious for larger or less detailed models. Resin printing, while often more expensive initially and in materials, delivers higher detail and smoother finishes, ideal for intricate parts. Think about your priorities: if you need quick, affordable prototypes, FDM might be better. If you require precision and fine details, resin could be worth the investment. Additionally, understanding filtration systems and their role in maintaining a safe workspace is important, especially when working with resin materials that can produce hazardous fumes. Incorporating layer precision considerations can also influence which method is more suitable for your project’s requirements.
What Common Mistakes Should You Avoid When Choosing Between FDM and Resin?
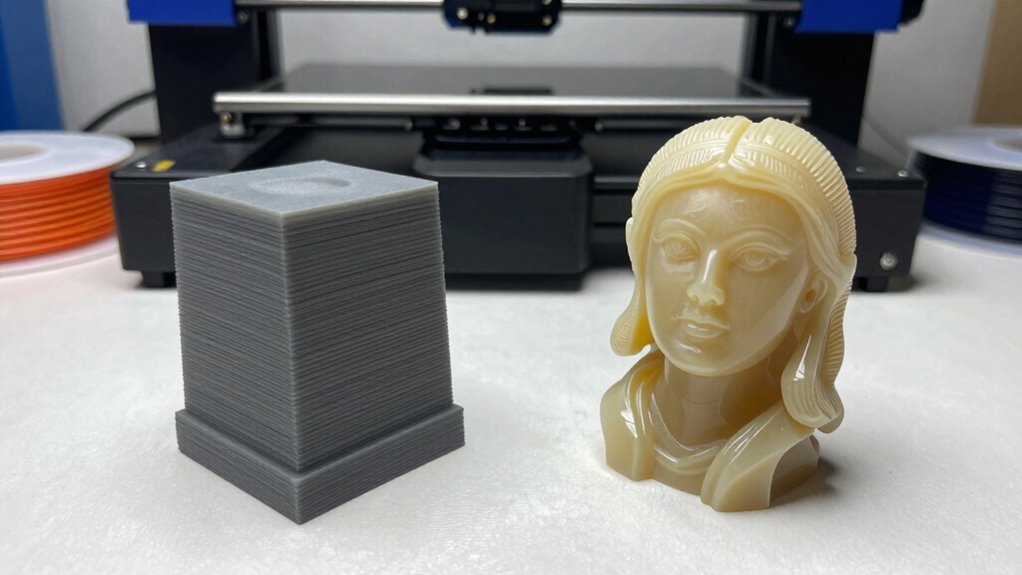

When selecting between FDM and resin 3D printing, one common mistake is not thoroughly evaluating the specific requirements of your project. Ignoring material compatibility can lead to failed prints or subpar quality, especially if the chosen material isn’t suited for your application. Environmental considerations also matter—resin printers often involve fumes and require proper ventilation, while FDM uses filaments that may be more eco-friendly. To help, consider this comparison:
| Aspect | FDM | Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Wide range of thermoplastics | Limited to photopolymer resins |
| Environmental Impact | Less fumes, easier cleanup | Fumes and chemical waste |
| Post-processing | Minimal, easier cleanup | More involved, requires curing |
Additionally, understanding the material properties can significantly impact your project’s success. Avoid these mistakes to ensure your choice aligns with your project’s needs and constraints.
When Should You Use FDM or Resin Printing? Real-World Use Cases
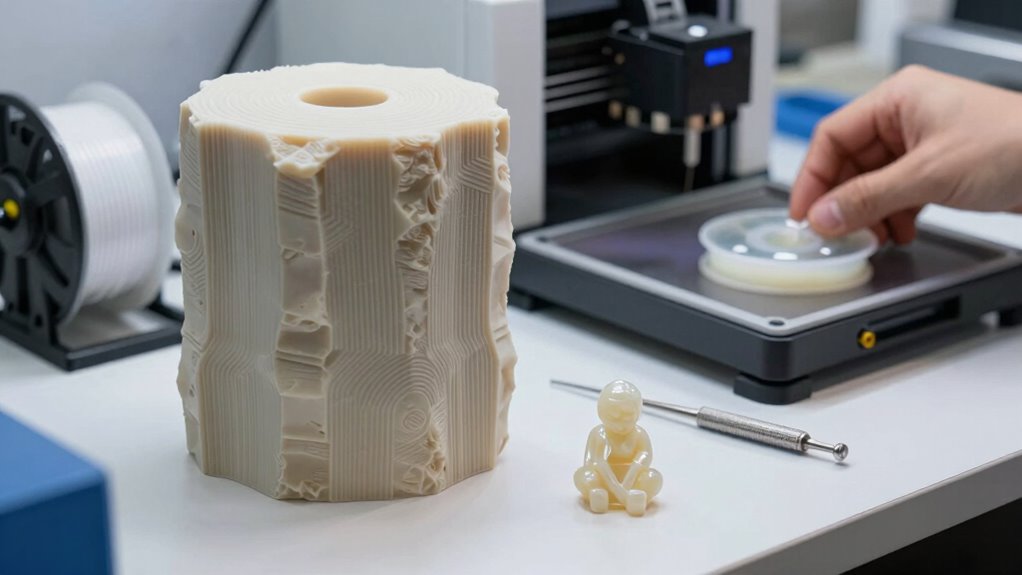

FDM and resin 3D printing each excel in different scenarios based on your project’s specific needs. If you prioritize material flexibility, FDM is ideal for larger prototypes or functional parts that require durability and a wide range of filament options. It’s also a better choice if environmental impact matters, as FDM filaments are generally more eco-friendly and easier to recycle. Resin printing shines when you need high-resolution, detailed models, like jewelry, dental, or miniatures. However, resin’s environmental impact is higher due to the chemicals used and the need for proper disposal. Use FDM for cost-effective, larger builds with moderate detail, and opt for resin when precision and fine surface finishes take precedence over environmental considerations.
Final Tips for Making an Informed 3D Printing Decision Without Regrets

To make an informed 3D printing decision without regrets, start by clearly defining your project’s main requirements—whether that’s detail, strength, cost, or environmental impact. Consider the material cost, as resin often has higher expenses for resin and maintenance, while filament tends to be more budget-friendly. Think about the environmental impact; resin printing produces chemical waste that’s harder to dispose of, whereas FDM uses biodegradable filament options. Match your priorities with the strengths of each method. If you need intricate details and can handle chemical waste, resin might suit you best. For larger, more durable parts on a budget with less environmental concern, FDM is likely the better choice. Making these considerations upfront helps avoid regrets and ensures your project’s success. Additionally, evaluate the ease of use and setup for each method to ensure it aligns with your skill level and available resources. Understanding the learning curve associated with each technology can also prevent frustration and help you select the most suitable option for your experience level.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Environmental Impacts of FDM and Resin 3D Printing?
You should consider the environmental impacts of FDM and resin 3D printing. FDM uses plastic filaments, which can be recycled, but not all recycling options are accessible or practical. Resin printing involves toxic materials that require careful handling and disposal, increasing environmental risks. Both methods generate waste, but resin’s material toxicity makes it more concerning if you don’t follow proper disposal procedures. Always research recycling options and handle materials responsibly.
How Safe Are FDM and Resin Printers During Operation?
During operation, your FDM printer is generally safe, but you should still avoid inhaling filament fumes and guarantee proper ventilation for FDM safety. Resin printers pose more risks, as resin toxicity can cause skin and eye irritation, so wearing gloves and eye protection is essential. Always operate in a well-ventilated area, follow safety guidelines, and handle resins carefully to minimize health hazards.
Can FDM or Resin Printers Be Used for Large-Scale Manufacturing?
Think of scaling as building a bridge—your choice of printer matters. FDM printers excel in large-scale manufacturing because they handle bigger volumes and have better material availability, easing scaling challenges. Resin printers, while precise, struggle with size limitations and higher costs. So, if you aim for mass production, FDM is your best bet; resin’s better suited for detailed, small-batch parts.
What Are the Best Cleaning and Maintenance Practices for Each Method?
You should follow proper post-processing protocols to keep your printers in top shape. For FDM, regularly clean the nozzle and bed, check for filament jams, and lubricate moving parts. Resin printers require careful cleaning of the build platform and resin vat, plus thorough curing of prints. Consistently maintain equipment by inspecting for wear, replacing filters, and calibrating components, ensuring reliable performance and high-quality results.
How Do I Choose the Right Printer Brand and Model for My Needs?
You need to consider brand reputation and cost analysis when choosing a 3D printer. Think about which brands consistently deliver quality, durability, and good customer support—these often stand out in reviews. Then, compare costs, including upfront price, maintenance, and filament or resin expenses. By doing this, you’ll find a model that fits your needs without surprises, making your investment smarter and more satisfying in the long run.
Conclusion
Choosing between FDM and resin 3D printing isn’t just about specs—sometimes, the perfect fit reveals itself unexpectedly. Trust your project’s needs, but stay open to surprises, as the right technology might align when you least expect it. In the end, your choice shapes your results, and coincidence might just guide you to the method that feels almost destined. Embrace the journey, and you’ll find the perfect print, no regrets involved.








